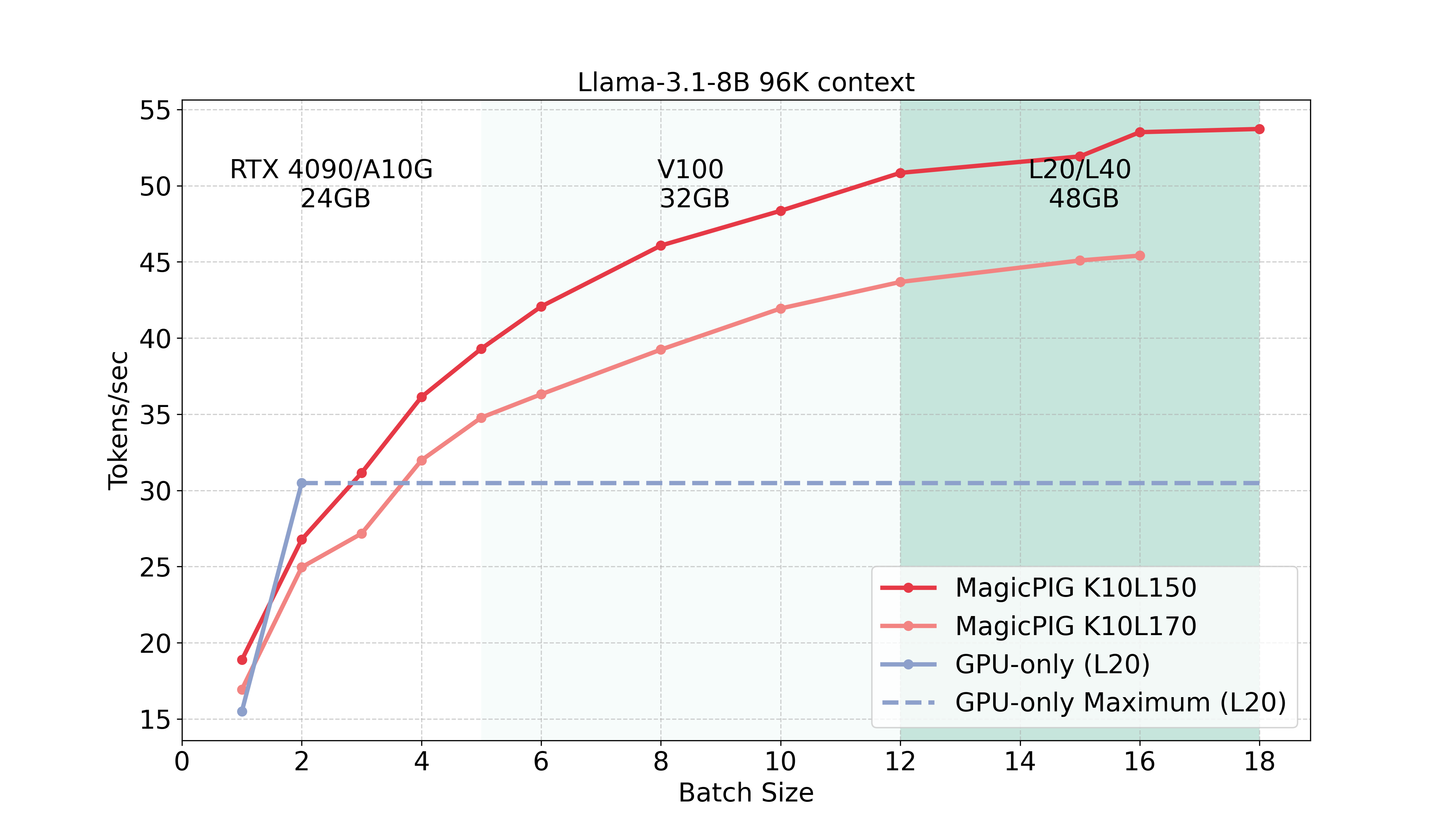
MagicPIG leverages sampling for efficient attention estimation, utilizing CPUs as augmented memory to significantly enhance inference throughput. This approach stands out by combining computational efficiency with scalability, making it well-suited for handling resource-intensive tasks. Unlike conventional TopK attention mechanisms, which can struggle with maintaining both precision and performance as context lengths grow, MagicPIG excels in processing complex tasks such as long-context reasoning. By effectively distributing memory and computation between CPUs and accelerators, MagicPIG not only ensures high throughput but also maintains the fidelity of attention mechanisms over extended sequences.
Zhuoming Chen, Ranajoy Sadhukhan, Zihao Ye, Yang Zhou, Jianyu Zhang, Niklas Nolte, Yuandong Tian, Matthijs Douze, Leon Bottou, Zhihao Jia, Beidi Chen
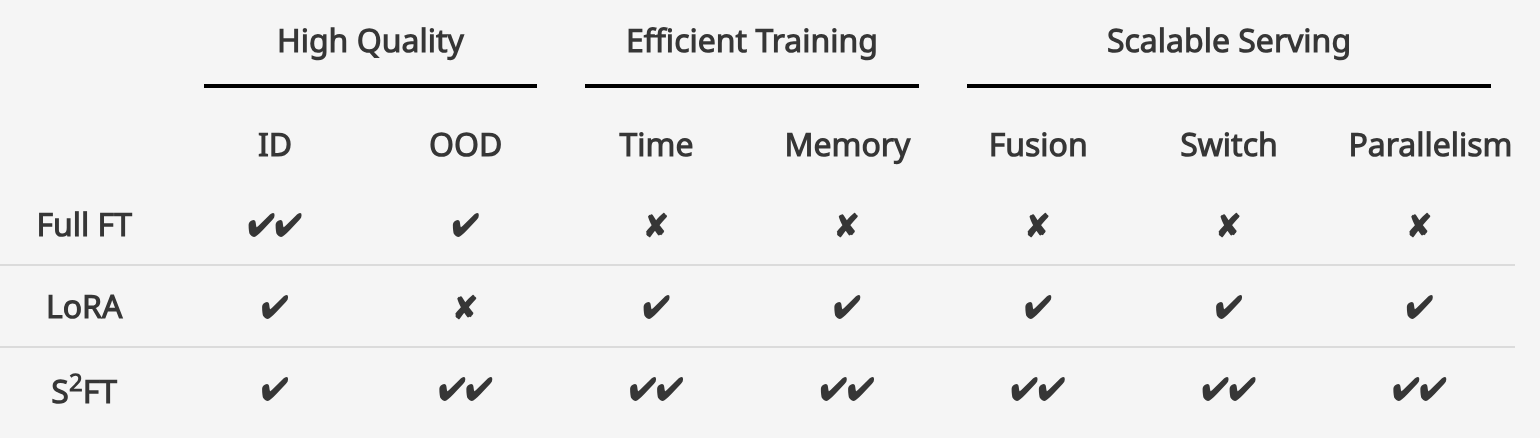
Structured Sparse Fine-Tuning (S2FT) is a novel PEFT family for LLMs that achieves high quality, efficient training, and scalable serving simultaneously. It accomplishes this by “selecting sparsely and computing densely”. Compared to LoRA,S2FT enhances generalization ability on both commonsense and arithmetic reasoning with 4.6% and 1.3% average improvements while reduce 10% training time and memory. Furthermore, S2FT’s enables scalable effective fusion, fast switch, and efficient parallelism for serving multiple adapters. These features make S2FT particularly valuable for the large-scale, real-world deployment of foundation models in various domains.
Xinyu Yang, Jixuan Leng, Geyang Guo, Jiawei Zhao, Ryumei Nakada, Linjun Zhang, Huaxiu Yao, Beidi Chen
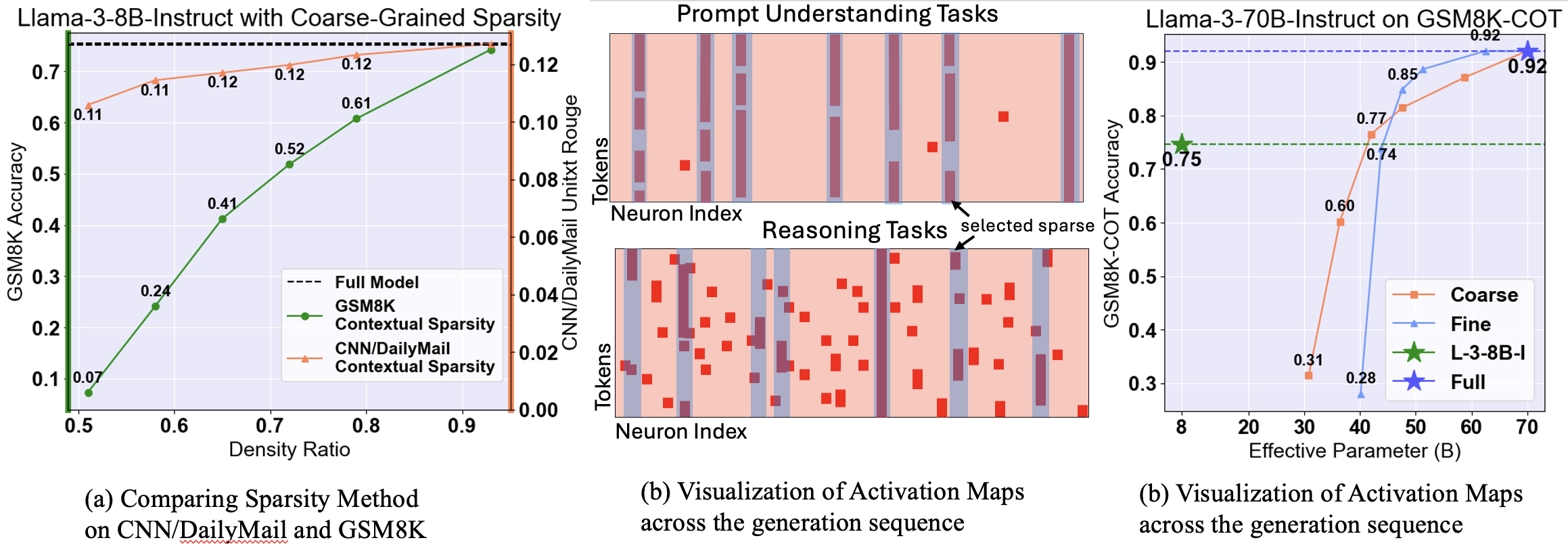
Contextual Sparsity (CS) is appealing for its training-free nature and its ability to reach a higher compression ratio seemingly without quality degradation. However, in this paper, we find that although CS succeeds in prompt-understanding tasks, CS significantly degrades the model performance for reasoning, deduction, and knowledge-based tasks. This paper introduces Sirius, an efficient correction mechanism, which significantly recovers CS models quality on reasoning tasks while maintaining its efficiency gain. We comprehensively evaluate Sirius on 6 models across 8 complex generation tasks. Also, we develop system implementation for Sirius to achieve around 20% speedup for Llama-3-8B-Instruct on-chip and 35% on Llama-3-70B-Instruct offloading.
Yang Zhou; Zhuoming Chen; Zhaozhuo Xu; Victoria Lin; Beidi Chen
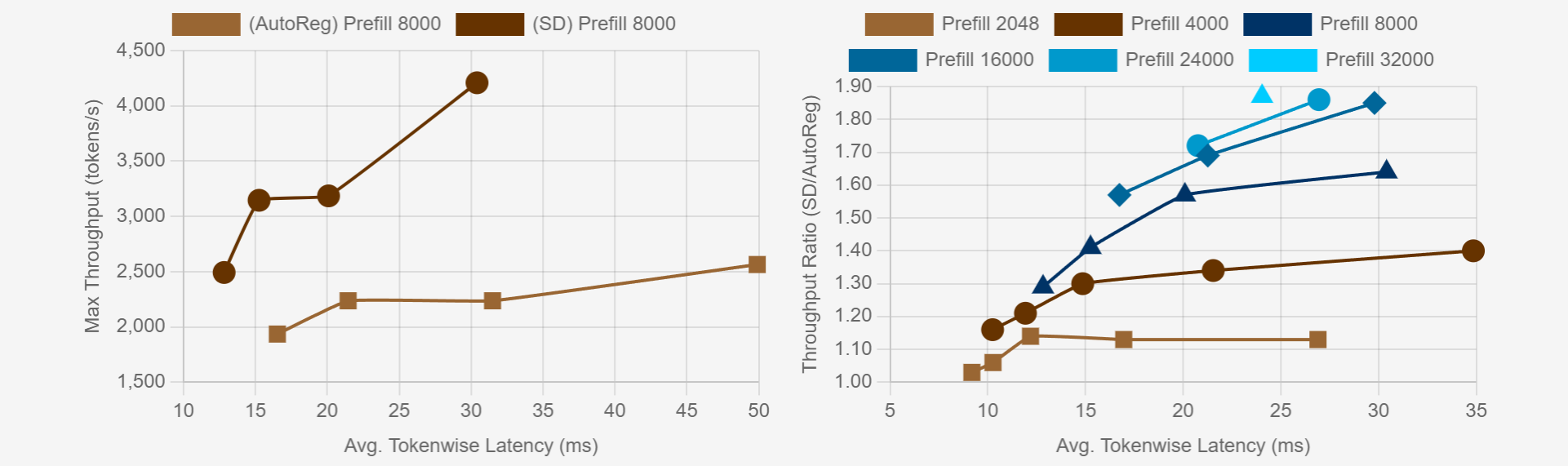
MagicDec studies the speculative decoding in the regime of long context and large batch serving and illustrate the potential of speculative decoding in improving throughput. MagicDec also proposes to use sparse attention for draft models, which is of vital importance for large batch serving. For moderate to long sequences, we demonstrate up to 2x speedup for LLaMA-2-7B-32K and 1.84x speedup for LLaMA-3.1-8B when serving batch sizes ranging from 32 to 256 on 8 NVIDIA A100 GPUs.
Jian Chen, Vashisth Tiwari, Ranajoy Sadhukhan, Zhuoming Chen, Jinyuan Shi, Ian En-Hsu Yen, Avner May, Beidi Chen

MagicDec studies the speculative decoding in the regime of long context and large batch serving and illustrate the potential of speculative decoding in improving throughput. MagicDec also proposes to use sparse attention for draft models, which is of vital importance for large batch serving. For moderate to long sequences, we demonstrate up to 2x speedup for LLaMA-2-7B-32K and 1.84x speedup for LLaMA-3.1-8B when serving batch sizes ranging from 32 to 256 on 8 NVIDIA A100 GPUs.
Jian Chen, Vashisth Tiwari, Ranajoy Sadhukhan, Zhuoming Chen, Jinyuan Shi, Ian En-Hsu Yen, Beidi Chen
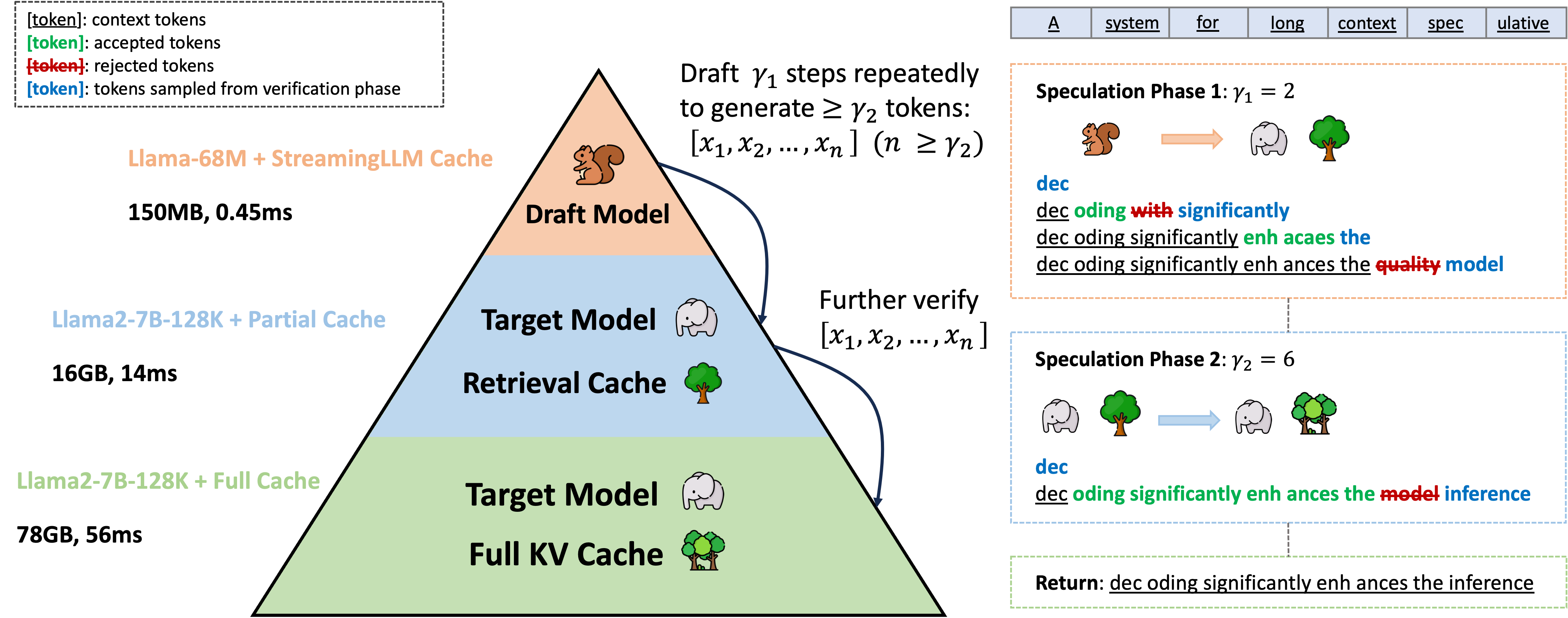
With large language models (LLMs) deployed for long content generation, the growing key-value (KV) cache size has become a bottleneck, leading to low computational core utilization and high latency. TriForce, a hierarchical speculative decoding system, addresses this by using dynamic sparse KV cache via retrieval and a smaller model for speculative decoding, achieving up to 2.31× speedup on an A100 GPU and notable efficiency on RTX 4090 GPUs. TriForce also outperforms DeepSpeed-Zero-Inference by 4.86× on a single RTX 4090 GPU, maintaining robust performance across various temperatures.
Hanshi Sun, Zhuoming Chen, Xinyu Yang, Yuandong Tian, Beidi Chen
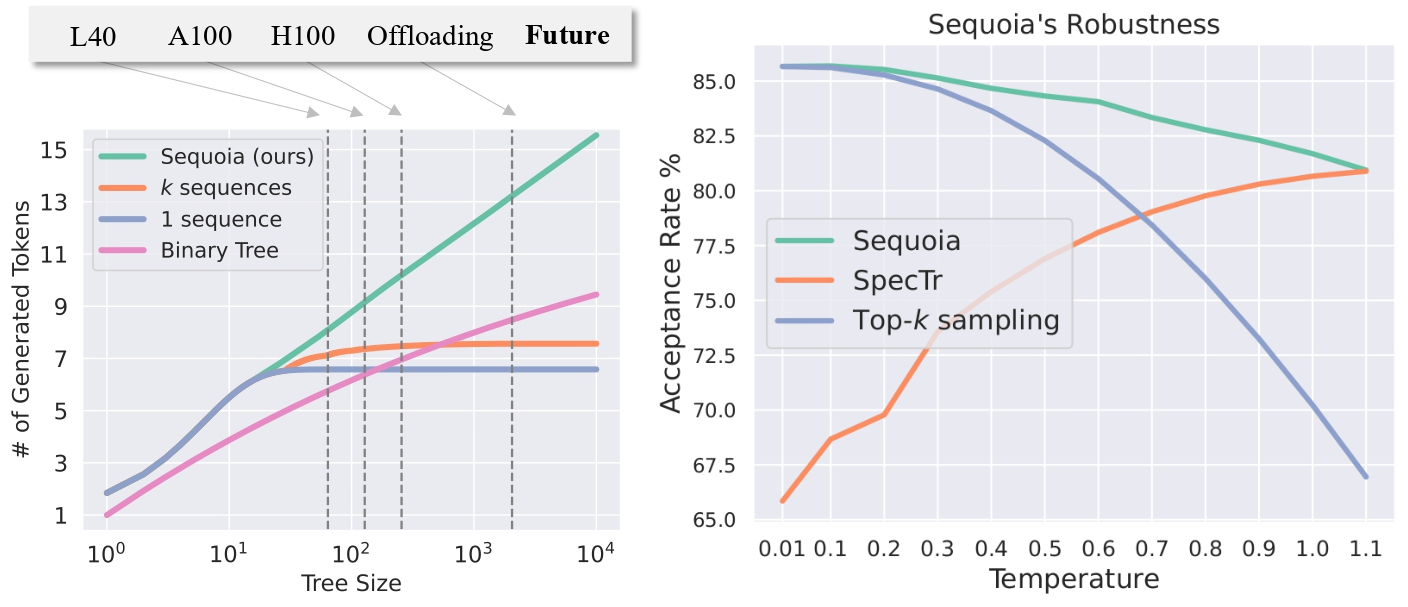
Sequoia offers a scalable, robust, and hardware-aware solution for speculative decoding. Sequoia uses a dynamic programming algorithm for optimal token tree structures, a novel sampling and verification method for robust performance across temperatures, and a hardware-aware optimizer for maximum efficiency. Evaluations show Sequoia significantly speeds up decoding, improving Llama2-7B, Llama2-13B, and Vicuna-33B performance on an A100 by up to 4.04×, 3.73×, and 2.27×, respectively, and achieving impressive speedups in offloading settings.
Zhuoming Chen, Avner May, Ruslan Svirschevski, Yuhsun Huang, Max Ryabinin, Zhihao Jia, Beidi Chen